5901 Botham Jean Blvd, Dallas, TX 75215
What is MRI Decommissioning and Why is it Important?
August 9, 2025MRI decommissioning is the careful, systematic process of removing a magnetic resonance imaging machine from service at a healthcare facility.
The procedure involves more than simply unplugging equipment. It requires specialized knowledge, careful planning, and strict adherence to safety protocols to protect both people and the environment.
When a facility decides to upgrade its imaging technology or close a department, proper decommissioning becomes essential. MRI machines contain powerful superconducting magnets cooled by liquid helium, along with potentially hazardous materials that require expert handling.
Without proper procedures, these components pose significant risks.
Why Professional MRI Decommissioning is Crucial
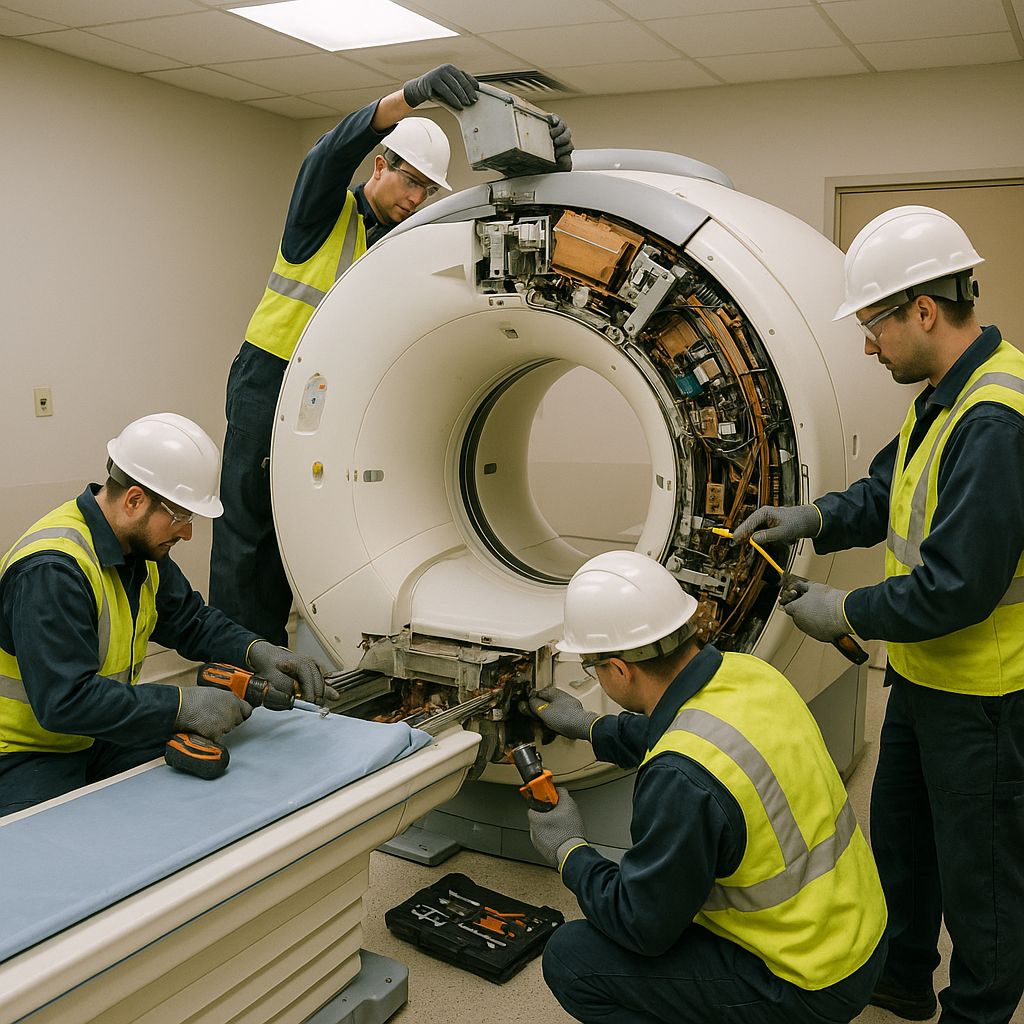

Professional MRI decommissioning is essential for several reasons. First, it ensures compliance with environmental regulations and healthcare standards. These machines contain materials that must adhere to strict disposal guidelines, and failing to comply can result in severe penalties.
Ensuring patient and staff safety is another critical aspect of proper decommissioning. The powerful magnets in MRI machines can turn ordinary objects into dangerous projectiles if not powered down correctly. The quenching process—where the magnetic field is deliberately collapsed—must be managed with extreme care to prevent injury, equipment damage, and facility disruption.
From an environmental perspective, responsible decommissioning prevents hazardous materials from contaminating soil and water supplies. Proper containment and disposal of components containing mercury, beryllium, and other potentially harmful substances protect communities surrounding healthcare facilities.
Lastly, proper decommissioning enables resource recovery. These sophisticated machines contain valuable materials, including copper, aluminum, and rare earth elements that can be recycled and reused in manufacturing new equipment. This approach not only reduces waste but also supports sustainability within the medical technology sector.
Cost Considerations in MRI Decommissioning
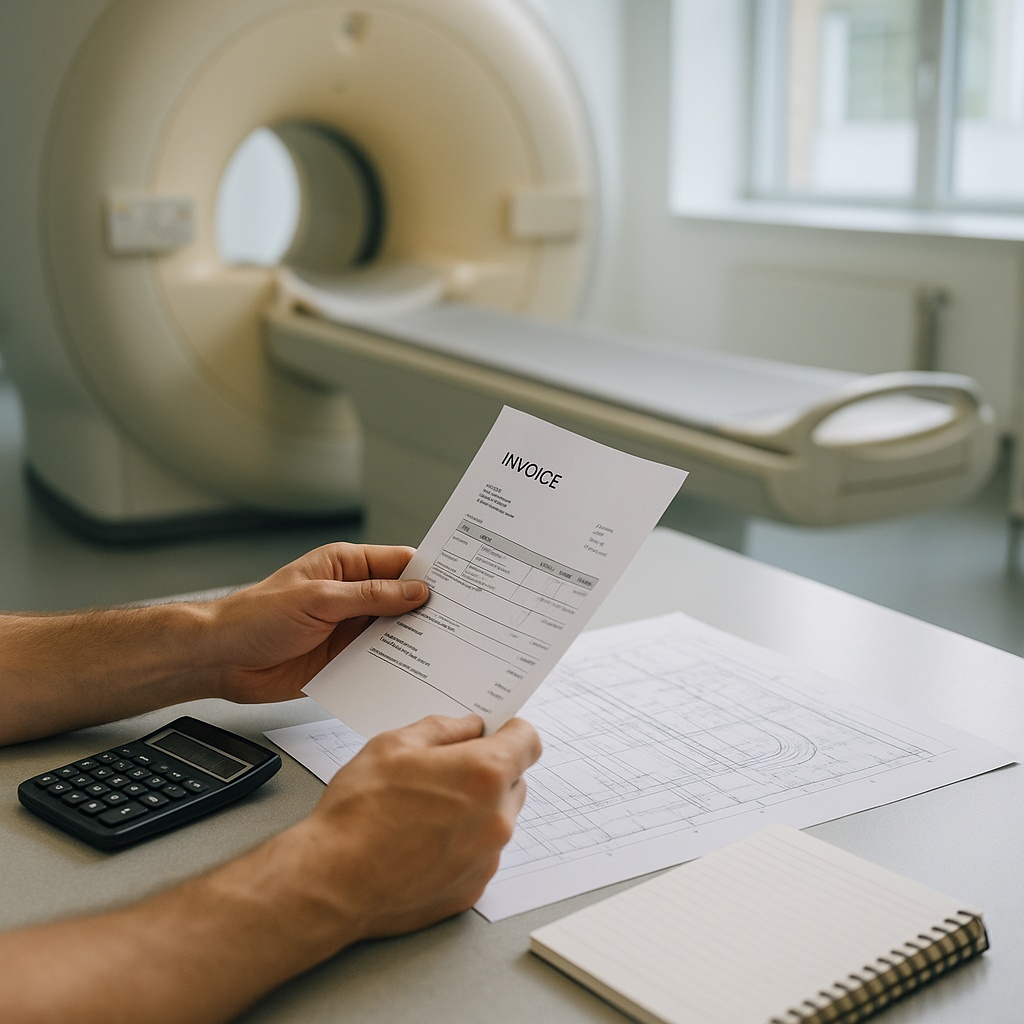

The financial aspect of MRI decommissioning involves more than just the initial service fee. Several cost factors affect the overall budget. Understanding these can help healthcare facilities plan effectively, avoid unexpected overruns, and potentially recover value from the decommissioning process.
Machine Size, Age, and Technology
Larger, high-field MRI units require more complex dismantling procedures and specialized handling equipment, which increase labor and transport costs. Older machines may have outdated components that are harder to recycle, while newer models can yield more valuable recoverable materials.
Location and Facility Access
MRIs located in urban hospitals with freight elevators and dedicated loading docks are easier to remove than those in older buildings with narrow hallways or no knockout panels. Sometimes, exterior wall removal or crane services may be necessary, significantly adding to costs.
Regulatory Compliance and Hazardous Material Handling
Compliance with environmental regulations and the safe handling of liquid helium, beryllium, or mercury-containing components require certified specialists. These services often involve additional fees but are essential for legal and environmental protection.
Material Recovery Value
Market prices for copper, aluminum, and rare earth elements can offset costs. Facilities that partner with experienced recyclers can maximize returns from extracted materials, lowering net decommissioning expenses.
Safety Protocols for MRI Decommissioning Teams
Removing an MRI machine poses significant safety risks due to powerful magnets, cryogens, and heavy components. Strict safety protocols are essential to protect workers, patients, and the facility during the process.
Magnet Quenching Procedures
The quenching process, where the superconducting magnet’s field is deliberately collapsed, must be handled by trained technicians. Improper quenching can cause helium to rapidly expand, leading to oxygen displacement and potential asphyxiation hazards.
Handling of Heavy and Oversized Components
The MRI magnet can weigh several tons. Rigging crews must use certified lifting equipment and follow safe rigging practices to prevent structural damage and injury. Clear communication between crane operators and ground crews is crucial.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Technicians require PPE such as cryogenic gloves, face shields, respiratory protection, and steel-toe boots. The choice of PPE is based on task-specific hazards identified during pre-job safety assessments.
Site Safety Coordination
Hospitals must coordinate with decommissioning teams to schedule work during low-traffic hours, restrict access to removal zones, and post clear warning signs to protect patients and staff.
Environmental Responsibility and Recycling in MRI Decommissioning
Proper disposal and recycling of MRI components are crucial for preventing environmental harm and promoting a circular economy. These machines contain both hazardous substances and highly valuable materials that need to be managed responsibly.
Hazardous Material Containment
Liquid helium, mercury-containing switches, and beryllium parts must be carefully removed and stored in approved containment systems. Mishandling these materials can contaminate soil and water, leading to costly remediation efforts.
Recycling High-Value Metals
MRI systems are rich in copper, aluminum, and rare earth elements, all of which can be reprocessed into new equipment. Recovering these materials reduces the need for mining and lowers the environmental impact of manufacturing.
Electronic Component Processing
Control panels, computers, and imaging electronics are sent to certified e-waste recyclers, ensuring safe extraction of metals like gold and silver while preventing toxic substances from entering landfills.
Documented Environmental Compliance
Partnering with certified recyclers ensures compliance with environmental standards and provides documentation proving that hazardous materials were disposed of legally and sustainably, protecting the healthcare facility from future liability.
What are the Key Steps in the MRI Decommissioning Process?
MRI decommissioning requires meticulous planning and specialized expertise to ensure safety, comply with regulations, and handle valuable components properly. The process involves several complex stages executed precisely.
Decommissioning an MRI machine is not a task for untrained personnel. These sophisticated devices contain hazardous materials and valuable components that require careful handling by experienced technicians. Each step addresses specific safety and environmental concerns.
1. System Powering Down
The first critical step is safely powering down the MRI system, which involves more than flipping a switch. Technicians must follow manufacturer-specific protocols to disconnect the machine from power sources and secure electrical boxes to prevent accidental surges or injuries.
For superconducting MRIs, this stage includes ramping down the magnetic field in a controlled manner. Improper shutdown can damage equipment and pose safety risks.
2. Hazardous Material Removal
MRI machines contain materials that must be removed and handled appropriately. The most significant is liquid helium, used as a cryogen to cool superconducting magnets to extremely low temperatures.
Specialized technicians must carefully remove these cryogens to prevent rapid expansion and pressure buildup. If helium transitions from liquid to gas too quickly, it can create dangerous pressure conditions. This step demands precision and the correct equipment to safely capture and contain the helium.
3. Careful Disassembly
After powering down the machine and removing hazardous materials, physical disassembly begins. This involves breaking down the MRI machine into its component parts, such as the gantry, patient table, electronics cabinets, and various subsystems.
For facilities without knockout panels, technicians might need to remove windows or doors to create a path for moving the disassembled components. The process requires careful planning of the exit route and consideration of the facility’s structural limits.
4. Component Sorting
After disassembly, components are sorted based on composition and recyclability. This is crucial for maximizing the recovery of valuable materials and ensuring proper disposal of non-recyclable parts.
Technicians categorize parts into groups such as electronic components, metals, plastics, and hazardous materials. Each category follows a different processing path to ensure environmental compliance and resource recovery.
5. Extraction of Valuable Materials
MRI machines contain significant amounts of valuable materials that can be recovered during decommissioning. The superconducting magnet contains niobium-titanium alloy wires embedded in copper, which can sell for $10-15 per pound.
Other recoverable materials include substantial amounts of copper and aluminum used throughout the machine. Advanced extraction techniques ensure these materials are properly recovered for recycling or reuse. Proper recovery not only has environmental benefits but can also offset some decommissioning costs.
6. Non-Recyclable Parts Disposal
Some components cannot be recycled and must be disposed of according to environmental regulations. This may include certain electronic parts, contaminated materials, or components that cannot be effectively separated.
Proper disposal involves working with authorized waste management facilities that can handle specialized medical equipment waste. Documentation of proper disposal is essential for regulatory compliance and environmental responsibility.
Throughout the decommissioning process, documentation must be maintained for inventory management and regulatory compliance. This includes records of the device’s condition, reasons for decommissioning, and the fate of all components.
The complexity of MRI decommissioning highlights the importance of working with experienced professionals who understand the technical, safety, and environmental aspects of the process. Cutting corners during decommissioning can lead to safety hazards, environmental violations, and the loss of potentially valuable recoverable materials.
When managed properly, MRI decommissioning can be accomplished safely while maximizing the recovery of valuable resources and ensuring full compliance with all relevant regulations.
[[artifact_table]]Valuable Materials Recovered from MRI Decommissioning[[/artifact_table]]
Conclusion: The Future of Sustainable MRI Decommissioning

As medical imaging technology continues to advance, the responsible decommissioning of MRI machines becomes crucial for our planet’s future. These machines house powerful magnets containing valuable materials, such as niobium-titanium alloys and rare earth elements, which can be recycled rather than discarded. By adopting efficient recycling methods, healthcare facilities can make a significant positive environmental impact while also realizing financial benefits.
Sustainable decommissioning of MRI equipment provides healthcare facilities with an important opportunity to support a circular economy. Effective recycling minimizes waste and maximizes material reuse, reducing the demand for environmentally damaging mining practices. Healthcare organizations that embrace responsible MRI disposal strategies not only reduce their ecological footprint but also demonstrate environmental stewardship. This approach aligns with the broader movement toward sustainable healthcare, balancing quality patient care with environmental responsibility. For those concerned about the future of healthcare and our planet, Okon Recycling can be contacted at 214-717-4083.
