5901 Botham Jean Blvd, Dallas, TX 75215
Breaking Down a Large AC Unit: What Can Be Recycled?
May 1, 2025Did you know that nearly 90% of an air conditioning unit‘s components can be recycled? Large commercial AC systems contain valuable materials that, when properly processed, can be repurposed instead of ending up in landfills.
Metals constitute the most significant recyclable portion of any AC unit. Copper tubing and wiring, aluminum coils, and steel casings are highly sought after by recyclers. These metals retain their properties through multiple recycling cycles.
In addition to metals, other valuable components can be recycled. Circuit boards contain recyclable electronic elements, while hard plastics from casings and components can serve as raw materials for new products. Condensers, motors, coils, and brass parts all hold recycling potential when appropriately processed.
What Are the Key Components That Can Be Recycled?
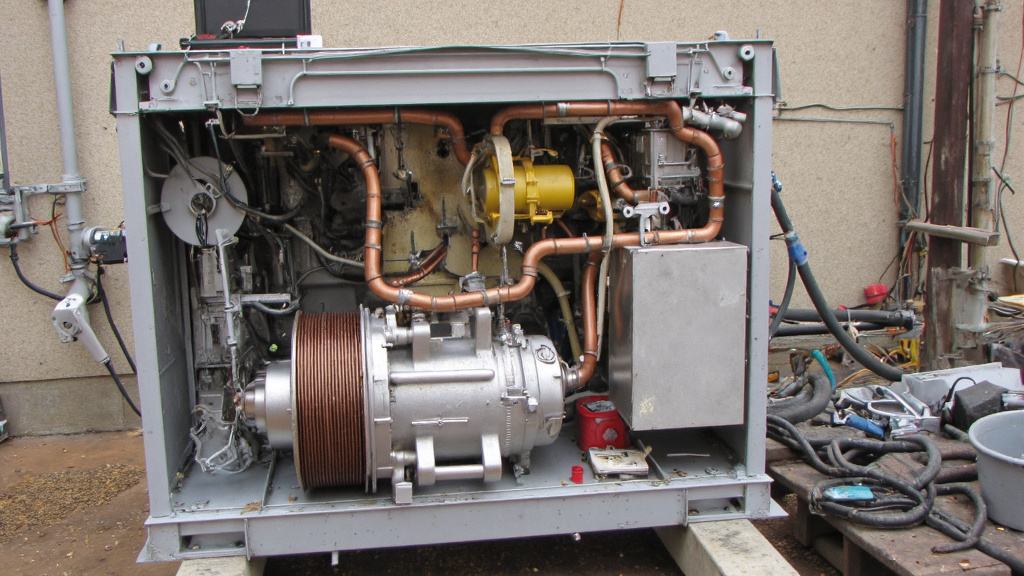
Large air conditioning units contain numerous valuable materials that can be recovered through proper recycling processes. When these units reach the end of their useful life, separating and recycling their components helps conserve natural resources and reduces landfill waste. Understanding what can be recycled is the first step toward responsible disposal.
Metals: The Valuable Core of AC Units
Metals make up a significant portion of air conditioning units and are highly prized in recycling markets. These materials can be extracted and processed repeatedly without losing their properties.
- Copper: Found in coils, wiring, and tubing, copper is one of the most valuable recyclable metals in AC units. Recycling copper requires 85-90% less energy than mining new copper.
- Aluminum: Present in fins, condensers, and housing components, aluminum can be recycled indefinitely. The recycling process uses only 5% of the energy required to produce new aluminum.
- Steel: Used in frames, cabinets, and mounting hardware, steel recycling saves significant resources. For every ton of steel recycled, approximately 1.5 tons of iron ore are conserved.
These metals are particularly valuable because they can be melted down and repurposed into new products without degradation in quality. The Environmental Protection Agency notes that recycling metals from appliances like air conditioners helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with mining and processing raw materials.
Plastics: More Recoverable Than You Might Think
Modern air conditioners contain various plastic components that can be recycled into new products rather than sitting in landfills for centuries.
- Casings and Covers: Often made from ABS or polypropylene, these can be ground down and reformed into new plastic products.
- Insulation: Some plastic foam insulation can be recycled through specialized processes.
- Fan Blades: Usually made from durable plastics that can be processed and reused in manufacturing.
Recycling plastics from AC units helps reduce petroleum consumption and prevents these slow-degrading materials from contributing to landfill overflow. According to recycling experts, plastic recycling can save up to 88% of the energy required to produce plastic from raw materials.
Components and Accessories
Beyond the basic metals and plastics, several other components can be recycled when properly separated:
- Pipes and Tubing: Often made of copper or aluminum, these conduits can be completely recycled.
- Circuit Boards: Electronic components contain precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum that can be recovered through specialized e-waste recycling.
- Compressors: These contain multiple recyclable materials including metals and oils that can be separated and processed.
- Fans and Motors: The metal components can be recycled while other parts may be refurbished or recycled.
- Wiring: The copper inside electrical wiring is highly recyclable and valuable.
Proper separation of these components is crucial for maximizing material recovery. When components are mixed or contaminated, recycling becomes more difficult and less efficient.
| Material | Components | Environmental Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Copper | Coils, wiring, tubing | 85-90% less energy required than mining new copper |
| Aluminum | Fins, condensers, housing | Uses 5% of the energy required to produce new aluminum |
| Steel | Frames, cabinets, mounting hardware | Conserves approximately 1.5 tons of iron ore per ton recycled |
| Plastics | Casings, covers, insulation, fan blades | Reduces petroleum consumption; saves up to 88% of energy |
| Circuit Boards | Electronic components | Recovery of precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum |
| Compressors | Metals, oils | Recycling prevents environmental contamination |
The recycling industry has developed sophisticated methods to process these materials. Material recovery facilities use various techniques including magnetic separation for ferrous metals, eddy current separation for non-ferrous metals, and various density-based separation methods for plastics.
By recycling these components rather than sending them to landfills, we help conserve natural resources and reduce the environmental impact of manufacturing new products. The EPA estimates that recycling an air conditioner can yield up to 65 pounds of recyclable materials, making it an important part of waste reduction efforts.
How is the Refrigerant Handled During Recycling?
Refrigerant recycling starts with recovery. EPA-certified technicians use specialized equipment to extract refrigerant gases from air conditioning systems, refrigerators, and other cooling appliances. This initial step prevents the release of harmful gases into the atmosphere.
Only EPA-certified technicians are legally allowed to purchase, handle, and recycle refrigerants. This certification ensures that professionals managing these substances understand proper handling procedures and environmental regulations. Technicians must keep documentation of certification at their workplace and maintain these records for three years after they stop working in this capacity.
The extraction process involves connecting recovery equipment to the appliance and removing the refrigerant to specific evacuation levels mandated by regulations. Technicians use AHRI-certified recovery machines that can extract refrigerant up to ten times faster than conventional equipment, minimizing downtime for commercial operations.
After extraction, technicians test the recovered refrigerant to determine its composition and quality. This analysis helps identify contaminants and decide whether the refrigerant can be recycled or requires reclamation. Recycled refrigerant has limitations on its reuse.
According to EPA regulations, recovered refrigerant cannot be resold unless reclaimed by a certified reclaimer. Exceptions exist when the refrigerant is transferred to equipment belonging to the same owner or was previously used only in a motor vehicle air conditioning system and properly recycled.
For mid-sized appliances containing between 5 to 50 pounds of refrigerant, technicians must maintain detailed records. These records include the location and date of recovery, the type of refrigerant recovered, monthly quantities by type, and documentation of transfers for reclamation or destruction.
The reclamation process involves purifying the recovered refrigerant to meet specific quality standards. This process removes contaminants, moisture, and other impurities that could affect performance. The reclaimed refrigerant can then be reused in new systems, creating a more sustainable lifecycle for these gases.
| Refrigerant | Components | Uses | ODP | GWP | Eco-Friendly | Flammable | Phase-Out/Ban |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-12 | CFC | Refrigerators and air conditioners | 1.0 | 10900 | No | No | Banned in 1994 |
| R-22 | HCFC | Refrigerators and air conditioners | 0.055 | 1810 | No | No | Banned by 2030 |
| R-134a | HFC | Refrigerators and car air conditioning | 0 | 1430 | Somewhat | No | Phased out in some regions |
| R-290 | HC (Propane) | Refrigerators and air conditioners | 0 | 6 | Yes | Yes | |
| R-404A | HFC | Freezers and refrigerators | 0 | 3922 | No | No | |
| R-410A | HFC | Refrigerators and air conditioners | 0 | 2088 | Somewhat | No | Phased out by 2025 |
| R-450A | HFO | Refrigerators and car air conditioning | 0 | 547 | Yes | No | |
| R-454B | Difluoromethane and 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene | Air conditioners and heat pumps | 0 | 466 | Yes | Yes | |
| R-513a | HFO | Air conditioners and refrigerators | 0 | 573 | Yes | No | |
| R-600a | HC (Isobutane) | Residential and small commercial refrigerators | 0 | 3 | Yes | Yes |
What is the Process for Recycling a Large AC Unit?
Recycling a large air conditioning unit involves several critical steps to ensure environmental safety and proper materials recovery. The process begins with finding a qualified recycling service specializing in HVAC equipment. These professionals follow strict EPA guidelines to prevent harmful refrigerant release and maximize resource recovery.
Step-by-Step AC Recycling Process
The first step in recycling a large AC unit is contacting a qualified recycling company. These specialists offer either pickup services for bulky units or convenient drop-off locations for units you can transport yourself. Many municipalities also maintain directories of EPA-approved recycling centers that accept large appliances.
Before transportation, the unit must be safely disconnected from power sources and any mounting structures. Never attempt to disconnect central air systems yourself, as this requires professional expertise to prevent damage and injury.
Refrigerant removal is perhaps the most critical step in the process. The EPA mandates that all refrigerants must be properly extracted by certified technicians. Some recycling facilities handle this step in-house, while others require you to have an EPA-licensed professional remove the refrigerant before accepting the unit.
Following refrigerant extraction, technicians disassemble the unit to separate valuable materials. An average AC unit can yield up to 65 pounds of recyclable components, including copper, aluminum, steel, and various plastics. These materials are sorted for processing at specialized facilities where they’ll be transformed into new products.
Electronic components like circuit boards receive special handling to recover precious metals while safely disposing of potentially hazardous elements. Compressor oils are also carefully extracted and processed separately to prevent environmental contamination.
Professional Recycling Services
Professional recycling services offer significant advantages over attempting to dismantle an AC unit yourself. These companies employ EPA-certified technicians who understand the proper handling of refrigerants like R22 (Freon) and R401a, which can damage the ozone layer and contribute to global warming if released improperly.
Many recycling companies provide convenient pickup services, eliminating the need for you to transport heavy equipment. Some even offer documentation of proper disposal, which may be required for compliance with local regulations or for LEED certification in commercial buildings.
The EPA’s Responsible Appliance Disposal (RAD) program partners with utilities and retailers throughout the country to ensure safe removal and recycling of old appliances. These partners commit to properly handling all materials according to strict environmental protocols.
By choosing professional recycling services, you help prevent the release of harmful substances into the environment while ensuring valuable resources are recovered and reused. This responsible approach to AC disposal significantly reduces your environmental footprint and supports the circular economy.
Conclusion: Responsible Recycling of Large AC Units

Recycling large AC units is a vital environmental responsibility. These systems contain valuable metals like copper, aluminum, and steel that can be recovered and reused. Proper recycling conserves natural resources and prevents harmful refrigerants from escaping into the atmosphere, where they could contribute to ozone depletion and climate change.
The disposal process requires certified professionals to safely extract refrigerants, disassemble units, and ensure each component follows the correct recycling or disposal pathway. By choosing specialized recycling facilities, designated drop-off locations, or EPA-approved programs, we support a circular economy where today’s air conditioners become tomorrow’s resources.
For responsible AC unit recycling that protects the environment and maximizes material recovery, contact Okon Recycling at 214-717-4083.
