5901 Botham Jean Blvd, Dallas, TX 75215
What Are High-Powered Magnets and How Are They Recycled?
July 1, 2025High-power magnets represent the pinnacle of magnetic technology. These extraordinary devices, crafted primarily from rare earth elements, generate magnetic fields much stronger than conventional magnets. Their impressive strength stems from a unique composition that includes elements like neodymium, iron, boron, samarium, and cobalt.
Rare earth magnets fall into two main categories: neodymium magnets (NdFeB) and samarium-cobalt magnets (SmCo). Neodymium magnets currently hold the title of the world’s strongest permanent magnets. A small neodymium magnet can lift objects many times its own weight, greatly impacting numerous industries with its strength.
High-power magnets stand out from traditional options like ferrite or alnico magnets due to their energy product, a measurement indicating a magnet’s performance capability. While a standard refrigerator magnet barely registers on this scale, rare earth magnets deliver exceptional power in compact forms. This combination of strength and size efficiency makes them indispensable components in modern technology.
Why Are High Powered Magnets Dangerous?

Disclaimer: High-powered magnets can cause serious injury if not handled properly. The image above was taken for illustrative purposes. Do not attempt to handle strong magnets without proper safety precautions, including protective gloves and adequate spacing.
Unlike ordinary refrigerator magnets, high-powered magnets contain rare earth metals that create exceptionally strong magnetic fields. These magnets exert substantial attractive forces even from considerable distances and can snap together with enough force to crush fingers or other body tissues trapped between them.
The danger posed by these magnets is immediate and severe. They can collide forcefully enough to shatter on impact, creating sharp fragments that may cause injuries. Flying debris from broken magnets poses serious risks to eyes and other sensitive areas.
When mishandled, these magnets present distinct safety hazards. Intense pinching injuries can occur instantly when magnets attract across fingers or skin folds, often requiring medical attention and potentially causing lasting tissue damage.
Beyond physical injuries, these powerful magnets can disrupt electronics. Strong magnetic fields interfere with hard drives, credit cards, and navigation equipment. Placing them near laptops, smartphones, or other devices can permanently damage sensitive internal components.
Another major concern is their interference with medical devices. For individuals with pacemakers or implanted defibrillators, exposure to high-powered magnets can disrupt normal functioning, potentially creating life-threatening situations.
The Consumer Product Safety Commission has documented numerous cases where strong magnets have damaged expensive equipment and caused severe injuries. The danger extends beyond immediate physical risk. If swallowed, these magnets can attract across intestinal walls, causing perforations, blockages, and infections that require emergency surgery.
These risks are not theoretical. Since these products appeared on the market, thousands of injuries have been reported. Safety standards implemented in 2022 now require certain products with multiple loose magnets to be either too large to swallow or have weaker magnetic fields to reduce ingestion injuries.
For industrial settings where high-powered magnets are necessary, strict safety protocols must be established. Warning signs, protective equipment, and proper storage containers are essential to prevent accidents.
Despite safety improvements, vigilance remains crucial. The deceptively small size of many high-powered magnets belies their extraordinary strength and the serious dangers they present. Whether in homes, schools, or workplaces, understanding the unique risks of these magnets is essential for preventing injuries.
How Are High Powered Magnets Used in Modern Technology and Industry?
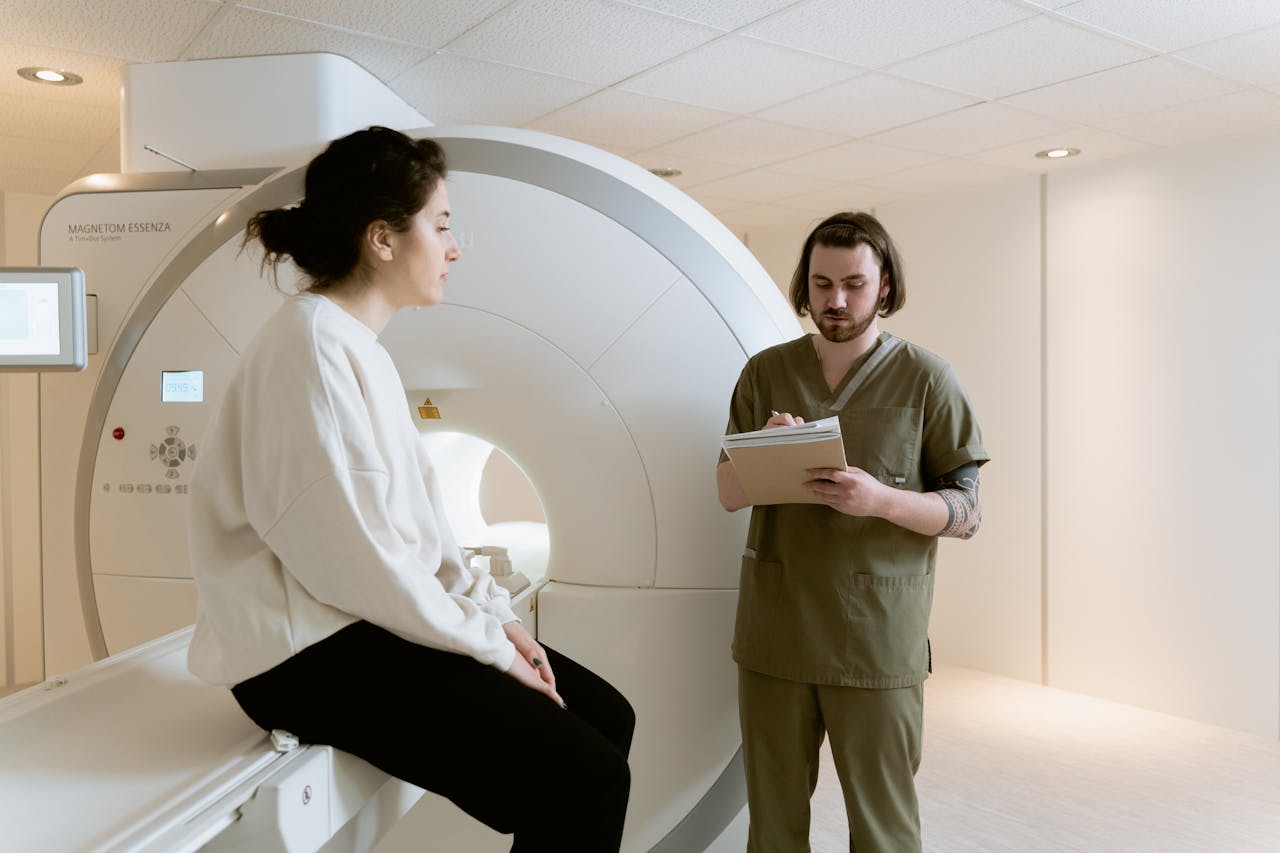
High-powered magnets are vital components in a wide range of industries. Their ability to produce strong magnetic fields makes them crucial for technological advancement and efficiency in various applications.
Manufacturing and Material Handling
In manufacturing facilities, high-powered magnets perform several essential functions. They facilitate efficient material handling with magnetic cranes, which lift heavy steel components without mechanical gripping mechanisms. This greatly reduces the time required for loading and unloading operations.
Construction sites use these powerful magnets to lift steel beams and other materials with precision. The magnets stabilize materials during welding or assembly, allowing workers to focus on accuracy rather than manual stabilization.
Recycling centers use industrial magnets to separate ferrous metals from non-metallic materials. This automation has transformed waste management by making the sorting process more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Medical Technology Applications
One of the most significant uses of high-powered magnets is in medical imaging technology. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machines employ powerful magnets to generate detailed images of internal body structures. These magnets create a strong magnetic field that aligns hydrogen atoms in the body, producing clear images that assist doctors in accurate diagnosis.
In addition to imaging, magnets play key roles in medical devices like pacemakers. Some therapeutic applications use magnets to relieve pain and enhance blood flow in specific treatments.
Energy Generation and Transportation
The energy sector has integrated high-powered magnets to enhance efficiency. Wind turbines and hydroelectric dams utilize these magnets in their generators to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy more effectively. The spinning blades turn shafts connected to magnets, creating magnetic fields that produce electricity.
Transportation technology has been transformed by high-powered magnets. Electric vehicles depend on them for motors and generators that provide propulsion and energy regeneration. Maglev trains use magnetic levitation to float above tracks, reducing friction and allowing speeds exceeding 300 mph while consuming less energy.
Electronics and Computing
High-powered magnets are fundamental components in speakers, headphones, and microphones, converting electrical signals into sound by precisely moving components in response to changing magnetic fields.
Computer hard drives have historically used magnets to store digital information, though solid-state storage is increasingly taking over this role. Many modern electronic devices incorporate magnets for various functions, from securing components to enabling features like automatic sleep when closing a laptop lid.
Industrial robotics systems utilize magnets in motors, actuators, and sensors. Neodymium magnets are particularly valuable in robotic arms and precision manufacturing systems due to their reliability and compactness. These magnets enable robots to perform complex tasks with remarkable precision and speed.
Energy Efficiency Improvements
One of the greatest advantages of high-powered magnets is their ability to enhance energy efficiency across various systems. By providing stronger magnetic fields with lower power requirements, these magnets help reduce energy consumption in motors, generators, and other electromagnetic devices.
Modern electric motors using high-powered permanent magnets can achieve efficiency ratings exceeding 90%, significantly higher than conventional motors. This translates to substantial energy savings in applications ranging from industrial equipment to household appliances.
Continuing advancements in magnetic materials expand applications in energy-efficient technologies. Research on rare-earth element-doped magnets aims to improve performance at extreme temperatures, crucial for specialized applications in deep-sea operations and space exploration.
As global demand for energy-efficient and sustainable technologies grows, high-powered magnets will play an increasingly vital role in industrial innovation. Their unique properties enable technological advancements that would otherwise be unattainable, making them essential components of modern technology.
What Happens to High-Powered Magnets After Use?
Despite their long-lasting utility, high-powered magnets eventually reach a point where they’re no longer viable for their original purpose—whether due to wear, demagnetization, or equipment upgrades. Given their rare-earth content and environmental impact, proper disposal or recycling is critical.
Unfortunately, these magnets are often discarded as electronic or industrial waste, ending up in landfills where their valuable materials go unrecovered. This disposal not only wastes critical rare earth elements like neodymium and samarium but also poses environmental risks due to potential leaching of heavy metals from associated electronic components.
The good news? High-powered magnets are recyclable. Specialized recycling facilities can extract rare earth elements and other valuable metals through advanced processes such as hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy. These recovered materials can then be reused in new magnets, batteries, or clean energy technologies, reducing the need for mining and supporting a circular economy.
Because rare earth mining is environmentally intensive and geopolitically complex, recycling used magnets offers a strategic and sustainable alternative. Industries that regularly use MRI machines, electric motors, or wind turbines can significantly reduce waste and resource strain by partnering with dedicated recyclers.
Conclusion: Recycle High-Powered Magnets Responsibly with Okon Recycling

High-powered magnets are indispensable in modern technology—but they also present unique disposal challenges. From medical imaging and renewable energy to robotics and transportation, these magnets contain valuable rare earth elements that should never be wasted.
Okon Recycling offers safe, responsible, and efficient recycling services for high-powered magnets and other industrial components. We understand the complexities of rare-earth materials and have the expertise to reclaim these resources while ensuring full environmental compliance.
Have magnets from MRI machines, electric motors, or industrial equipment? Contact Okon Recycling today at 214-717-4083 to recycle high-powered magnets safely and sustainably. Preserve resources, reduce waste, and support a greener future—one magnet at a time.
