5901 Botham Jean Blvd, Dallas, TX 75215
What is Magnet Waste Management?
April 30, 2025Did you know that over 100,000 tons of rare earth magnets are produced annually, with global demand expected to increase tenfold by 2050? Magnet waste management addresses this growing challenge through specialized techniques for handling, processing, and recycling discarded magnetic materials.
Magnet waste management involves the responsible disposal and recycling of magnets found in everything from smartphones to industrial equipment. These magnets contain valuable rare earth elements like neodymium and dysprosium that require special handling to prevent environmental contamination. Improperly discarded, these materials can leach into soil and waterways, creating potential hazards.
The process includes collection, sorting, processing, and material recovery techniques designed to minimize environmental impact while reclaiming precious resources. As technologies advance and sustainability becomes more important, proper magnet waste management has become a critical component of modern recycling systems and circular economy initiatives.
Why is Proper Disposal of Magnets Important?
Improper disposal of magnets poses significant environmental risks. Magnets, especially neodymium ones, contain rare earth metals that can contaminate soil and water when discarded incorrectly. These elements leach into ecosystems, disrupting habitats and threatening wildlife.
The environmental damage goes beyond pollution. Rare earth mining is resource-intensive. When magnets end up in landfills, we waste these valuable materials and increase demand for new mining, creating a cycle of environmental degradation.
Safety hazards are another concern. Strong magnets attract metal objects unexpectedly, causing injuries. When powerful magnets snap together, they can pinch or break fingers. This risk increases with improperly discarded magnets encountered by unsuspecting individuals.
Wildlife faces particular dangers from discarded magnets. Small animals may ingest these objects, resulting in internal injuries or death. Magnetic properties can cause severe blockages and perforations in their digestive tracts.
Electronic interference represents another risk. Magnets can damage nearby electronic devices, causing data loss or equipment failure. This is especially problematic when magnets are tossed into bins with other electronic waste.
For businesses, proper magnet disposal is not just environmentally responsible—it is a legal obligation. Companies that improperly dispose of magnets, particularly neodymium ones, may face fines and legal penalties for violating waste management regulations.
Water system contamination presents a serious long-term threat. Magnets thrown into water bodies can release harmful compounds over time. These substances may enter drinking water supplies, creating potential health risks for communities.
While small fridge magnets might seem harmless, even these items should be handled properly at end-of-life. The cumulative impact of millions of improperly discarded magnets creates a significant environmental burden.
The good news is that magnets can be recycled and repurposed. Breaking them down into component parts allows these materials to be used again in new products, reducing waste and limiting the need for additional mining operations.
| Impact Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental Contamination | Improper disposal of magnets can lead to soil and water pollution, contaminating ecosystems and drinking water. |
| Wildlife Harm | Magnets can be ingested by animals, causing internal injuries or death. |
| Human Safety Risks | Strong magnets can attract metal objects, causing injuries or damaging electronic devices. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Businesses must adhere to disposal regulations to avoid fines and legal consequences. |
| Recycling Benefits | Recycling magnets can reduce waste and the need for new mining operations, conserving resources. |
What Are the Best Practices for Magnet Disposal?
Proper magnet disposal is essential for environmental protection and safety. Strong magnets pose unique challenges due to their magnetic properties and potential environmental impact. Following best practices ensures safe handling and minimizes harm.
Demagnetizing Before Disposal
Demagnetizing magnets is a crucial first step in the disposal process. This procedure weakens their magnetic properties, making them safer to handle. For household magnets, this can be difficult without specialized equipment.
Professional disposal services often use demagnetizing coils or strong alternating magnetic fields to reduce magnetic strength. This process is especially important for powerful neodymium magnets, which can cause injuries if improperly handled.
Thermal demagnetization is required by federal regulations for disposing of strong permanent magnets. This involves heating the magnet to reduce its magnetic force. However, this should only be done by professionals with proper equipment.
Separating Magnetic Materials
When disposing of multiple magnets, keep them separated to prevent them from attracting each other. Use non-magnetic spacers such as cardboard, plastic, or foam.
For magnets embedded in larger objects or electronics, separate the magnetic components from non-magnetic materials whenever possible. This allows for more targeted disposal methods for each material type.
Store separated magnets in steel containers to prevent them from attracting other metal objects or waste disposal equipment. This containment is crucial, particularly for strong magnets.
Proper Packaging for Disposal
For household magnets like refrigerator magnets, wrap them in multiple layers of paper or plastic before disposal. Place wrapped magnets in a sturdy container to prevent damage to other items.
Small kitchen magnets can be placed in small metal containers before adding them to regular household waste. This prevents them from attracting other metal objects in the waste stream.
Label packages containing magnets to alert waste handlers about the contents. This helps prevent unexpected accidents during waste processing.
Following Local Regulations
Disposal regulations vary by location. Contact your local waste management service or recycling center to understand specific requirements for magnet disposal in your area.
Many communities offer specialized e-waste collection events that accept items containing magnets. These ensure proper handling of potentially hazardous materials.
Businesses must adhere to regulatory guidelines for magnet disposal. Non-compliance can result in significant fines and legal consequences.
Specialized Disposal Options
Recycling is preferable to disposal when possible. Many magnets contain recyclable materials like iron, nickel, or cobalt. Contact local recycling facilities to check if they accept magnets for recycling.
For industrial applications involving large quantities of magnets, consult with manufacturers or professional waste management services. Large-scale disposal often requires specialized procedures to ensure safety and compliance.
Consider alternative options like donation to educational institutions or creative reuse. Schools, art studios, and science organizations can often put unwanted magnets to good use, reducing waste and extending their useful life.
How Can Magnets Be Recycled or Repurposed?
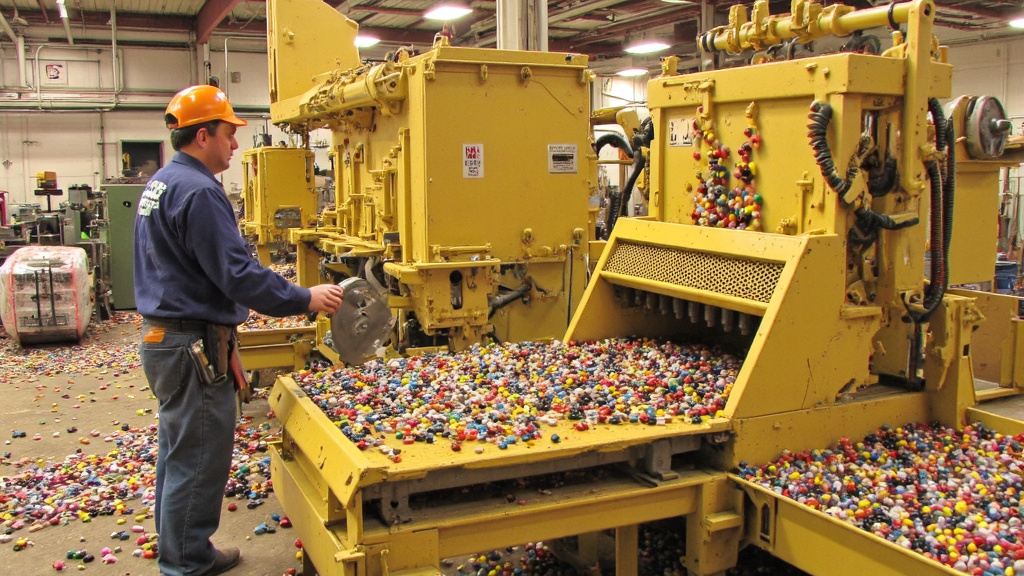

Magnets are integral to modern life, powering smartphones, computers, headphones, and electric vehicles. When these devices reach the end of their lifecycle, proper disposal of magnetic components is crucial for environmental sustainability. Fortunately, recycling and repurposing options exist for various types of magnets.
Recycling Rare Earth Magnets
Neodymium and other rare earth magnets require special handling for recycling. These powerful magnets contain valuable materials that should be recovered. However, less than 1% of rare earth elements have been recycled in recent years.
Professional recycling services use specialized processes to extract these materials. Hydrometallurgical processes have emerged as a promising recycling method, using aqueous solutions to dissolve and separate valuable elements from other materials.
Never dispose of strong neodymium magnets in regular trash or recycling bins. The Federal Government mandates that these magnets be thermally demagnetized before disposal, requiring heating them to about 176°F—their Curie point where magnetic properties diminish.
The easiest way to recycle rare earth magnets is to find a company specializing in handling them. Many local recycling centers accept these materials. Electronics stores and cell phone retailers often collect devices containing these magnets for proper processing.
Repurposing Magnets
Repurposing is another excellent alternative to disposal. Since magnets are neither recyclable in conventional systems nor biodegradable, reusing them extends their lifespan and keeps them out of landfills.
Consider these repurposing options:
- Re-cover promotional magnets with different images
- Create magnetic puzzles by cutting flexible sheet magnets
- Make custom fridge magnets by attaching small objects to disc magnets
- Donate magnets to schools or daycare centers for classroom projects
- Check with local scrap yards that might accept or pay for old magnets
Educational institutions often welcome magnet donations for science demonstrations and projects. Hobbyists and DIY enthusiasts can find creative uses for recycled magnets in home organization or craft projects.
Proper Disposal When Recycling Isn’t Available
If recycling options aren’t available, proper disposal becomes crucial. For ceramic or flexible sheet magnets, which are less powerful, disposal in regular trash is acceptable when necessary.
For stronger magnets, if you cannot find a recycling service:
- Try to demagnetize them first using appropriate tools
- If demagnetization isn’t possible, use iron or steel sheets to line a container
- Place the magnets inside the lined container for disposal
- This prevents magnets from sticking to other ferrous metals in landfills
Never give away powerful rare earth magnets as a means of disposal due to their potential hazards, as they can cause injury if not handled properly.
Benefits of Recycling Magnets
Recycling magnets, especially those containing rare earth elements, provides significant environmental and economic benefits. Producing new magnets can be environmentally damaging, involving mining practices that create toxic waste and radioactive byproducts.
By recycling magnets, we reduce the need for environmentally destructive mining while securing domestic supply chains for these critical materials. Companies specializing in magnet recycling can achieve impressive recovery rates—some reporting up to a 99.8% recovery efficiency for neodymium.
Recycled rare earth elements from magnets can be successfully reused in advanced technical equipment globally, creating a true circular economy for these valuable resources.
| Method | Process Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrometallurgical | Uses aqueous solutions to leach metals; involves leaching, purification, and recovery steps. | Lower energy consumption, selective metal recovery, reduced emissions. | Complex process, requires chemical handling. |
| Pyrometallurgical | Involves high-temperature smelting to separate metals; includes roasting, smelting, and refining. | Handles mixed feedstocks, effective at removing contaminants. | High energy consumption, limited metal recovery. |
As green technologies grow in popularity, the demand for rare earth elements is expected to increase significantly. Recycling these materials conserves resources, reduces environmental impact, and helps stabilize supply chains for critical industries.
Conclusion: The Future of Magnet Waste Management
Magnet recycling is crucial for resource conservation and environmental protection. With demand for rare earth elements projected to increase tenfold by 2050, effective magnet waste management is more important than ever. Innovative recycling techniques, such as hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical processes, provide viable alternatives to environmentally harmful mining practices.
These advanced methods achieve impressive results, with some technologies recovering over 95% of materials while using up to 95% less energy than primary production. As the recycling market grows—expected to reach $1 billion by 2030—we’re seeing a shift toward sustainable resource management that benefits both the environment and the economy.
Moving forward requires collaboration from all stakeholders. For businesses and organizations handling magnet-containing equipment, responsible disposal practices are essential. If your operation involves magnets from electronics, wind turbines, MRI machines, or other applications, contact Okon Recycling at 214-717-4083. Our expertise can help transform your magnet waste into valuable resources for the circular economy.
